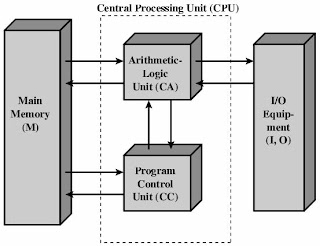
Control unit:
A control unit is circuitry that directs operations within
the computer's processor by directing the input and output of a computer
system. It controls the flow of
information through the processor, and coordinates the activities of the other
units within it. In a way, it is the "brain within the brain", as it
controls what happens inside the processor, which in turn controls the rest of
the PC. The control unit works by gathering input through a series of commands
it receives from instructions in a running programs and then outputs those
commands into control signals that the computer and other hardware attached to
the computer carry out.
One way to see the unity of control is to imagine a
conductor who gives orders to different orchestra musicians to synchronize and
get a whole coherent.
Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU)
The ALU (Arithmetic Unit and Logic) is the basic element of a microprocessor. As its name suggests, its role is to carry out arithmetic operations (addition, subtraction ...), logical (OR, AND, NOR ...), but also shift and transfer.
In its simplest form, it has an input connected to the data bus of the microprocessor, another connected to an internal register, and an output connected to the same register and data bus. It also has a bus for the selection of operations to perform.
The cycle for the execution of an operation is:
-Presentation of data on the first entry.
Select-load operation in the internal register. The data is thus conveyed to the output of the ALU loaded into the register, and presented on the second input.
-Presentation of new data on the first entry.
-Select the operation to perform.
Retrieving the result-output of the ALU and the data bus of the microprocessor.